Unit 3: Structure of Matter
1) Describe the characteristics of the major atomic models.
* Aristotle-
- Rip an item in half for infinity and it is still the same substance (atoms where
tiny sphere)
- Majority of people disagreed
- (hint- believes in a solid sphere)
- all matter is composed of tiny indestructible units, called atoms
- The atoms themselves remain unchanged but move about in space to combine
in various ways to form all objects
- Solid Sphere=
- He believed that you can divided an element many times but at some point the element would not be the same
* Dalton-
- (hint- believes in a solid sphere with a specific mass)
- Element consisted of tiny particles called atoms
- Elements are pure because all atoms were identical and have the same mass
- Atoms of each individual element are different from one another due to different masses
- Compounds have constant composition because they contain a fixed ratio of atoms and each atom has weight, thus fixing the weight ratio of one element to the other
- Dalton's model states atoms are tiny indestructible spheres with Specific Masses
ex: H-mass is 1
O-mass is 16
H2O- 1+1+16=mass of 18
Solid Sphere with Specific Mass
* J.J. Thompson-
- (hint- "plum pudding" model)
- An atom is composed of elements surrounded by a soup of positive charge to balance the electrons' negative charge like negatively charged "plums" surrounded by positively charged "pudding"
- Also, think of a chocolate chip cookie. The cookie part is negatively charged
and the chocolate chips are positively charged
* Rutherford-
- (hint- has a central nucleus surrounded by negative orbiting electrons- "crazy" electron cloud [picture is shown in upper right hand corner] - mass of the
atom is in the nucleus)
- Described the atom as having a central positive nucleus surrounded by
negative orbiting electrons
- Came to this conclusion following gold foil experiment
* Bohr-
- (hint- "neutrons and protons occupy in the nucleus-"organized" electron cloud)
- Electrons orbit the nucleus (like planets)
- Electrons occupy a fixed orbit
- Click here to watch a video on how to make
- Current models are mixture of Bohr and Rutherford's ideas.
What happens when you add or remove protons, neutrons, and electrons?
Protons- element changes, charge changes, mass changes
Neutrons- element stays the same, charge stays the same, mass changes
Electrons- element stays the same, charge changes, and mass stays the same
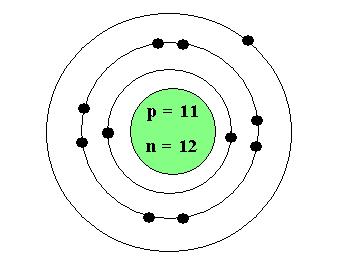
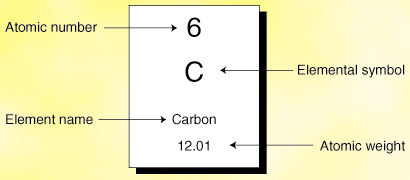
Atomic Number- is the whole number on the periodic table, tells the number of protons that element has
Electron- is found in the electrons cloud (rings). They do not have a mass. Each electron has a -1 charge.
Ion- an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons
Isotopes- atoms of particular elements that have a different number of neutrons than protons (more neutrons than normal)
Mass Number- is the decimal number on the periodic table, tells the number of protons and neutrons that are in the nucleus
Neutron- is found in the nucleus and has a mass. It does not change the charge of the atom. If you add or remove a neutron it will only change the mass.
Nucleus- found in the middle of an atom. Is made up of protons and neutrons
Proton- is found in the nucleus and has a mass. It does have a +1 charge for each proton. If you add or remove a proton it completely changes the element.
Valence Electrons- they are the electrons on the outmost ring. They are important for bonding.
How do you determine the number of valence electrons?
* The ones place in the group number
Why are they important?
* The valence electrons tells you how reactive that atom is and if it can bond.
Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes
Mass Location Charge
Proton
Neutron
Electron
1
1
0
Nucleus
Nucleus
Electron Cloud
+1
0
-1